What Is Total Productive Maintenance Explained Simply
Total productive maintenance (TPM) helps keep machines working their best. It aims to stop breakdowns, defects, and wasted time. This ensures smooth and steady work. For example, companies using TPM have fewer breakdowns—50% to 80% less. They also save 28% on maintenance costs. Reliable machines mean fewer stops and more work done. Nissan Electronics improved production by 25% in one year with TPM. By focusing on early care and teamwork, TPM changes how work is managed. It increases both safety and productivity.
What Is Total Productive Maintenance?
Definition and Purpose of TPM
Total productive maintenance (TPM) is a way to keep machines working well. It stops breakdowns, defects, and wasted time during production. Everyone in the company, like workers and managers, helps with TPM. This teamwork keeps machines running smoothly and avoids delays. It also boosts how much work gets done.
The goal of TPM is simple: keep machines running without problems. It finds issues early and fixes them before they get worse. Regular care saves money on repairs and keeps production steady. For example, TPM can cut maintenance costs by 30-50% and setup times by 90%. These changes make work faster and more efficient.
Goals of TPM in Modern Industries
Today’s industries use TPM to meet important goals. These goals help improve how work is done:
Eliminating bottlenecks: TPM makes workflows faster and smoother.
Reducing downtime: It stops machines from breaking unexpectedly.
Improving product quality: Machines make better products with fewer mistakes.
Extending equipment lifespan: Good care keeps machines working longer.
Here’s a table showing how TPM helps industries improve:
Metric | Improvement Percentage |
|---|---|
Less unplanned downtime | 80% |
More plant output | 31.5% |
Fewer process defects | 50-90% |
Annual savings on maintenance | $8.5 million |
These numbers show how TPM makes production better. Reliable machines mean more work gets done and costs go down.
Why TPM Is Essential for Operational Success
Industries need reliable machines to stay successful. TPM helps machines work their best and avoids delays. This improves how much work gets done and keeps customers happy with good products.
Studies show TPM methods, like fixing small problems early, improve performance. Companies using TPM see a 29.5% rise in Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) and a 51.5% drop in inventory levels. These results prove TPM helps companies stay ahead.
By solving machine problems early, TPM saves money and avoids delays. It also encourages workers to help improve machines. This teamwork makes work safer and more productive.
Tip: To start TPM, teach your team about its benefits. Get everyone involved in caring for machines.
Core Principles of Total Productive Maintenance
Overview of the 8 Pillars of TPM
The eight pillars of total productive maintenance (TPM) are its backbone. They help create a system where machines work their best. Each pillar focuses on improving a specific area, making production smoother and more reliable.
Here’s a simple look at the eight pillars:
Autonomous Maintenance: Lets workers handle basic care, needing fewer experts.
Planned Maintenance: Schedules repairs to avoid sudden machine failures.
Focused Improvement: Teams work to remove problems in processes.
Quality Maintenance: Fixes defect causes to ensure better product quality.
Early Equipment Management: Designs machines for easy care and efficiency.
Training and Education: Teaches workers skills to maintain equipment well.
Safety, Health, and Environment: Keeps workplaces safe while caring for machines.
Administrative and Office TPM: Uses TPM ideas to improve office tasks.
These pillars together build a strong TPM system. For example, car companies cut machine downtime by 30% using these methods.
Autonomous Maintenance and Employee Empowerment
Autonomous maintenance is a key part of TPM. It helps workers take charge of machine care. Simple tasks like cleaning and oiling stop small problems from growing bigger.
This method builds responsibility among workers. TPM training improves skills, making workers more confident. When employees feel capable, they help keep machines running better.
Here are some benefits of autonomous maintenance:
It creates a habit of fixing issues early.
Workers learn new skills and feel proud of their work.
Machines run longer without stopping, helping production.
For instance, one company reduced unplanned downtime by 48% and cut maintenance costs by 39%. This shows how involving everyone in care makes a big difference.
Continuous Improvement and Proactive Maintenance
Continuous improvement is a big part of TPM. It means making small changes often to improve machines and production. Proactive maintenance works with this by fixing problems before they cause breakdowns.
You can track progress using these key measures:
Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) | Checks machine availability, speed, and quality to see how well it works. |
Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF) | Measures how long machines run before breaking down. |
Mean Time to Repair (MTTR) | Tracks how fast repairs are done when machines fail. |
Planned Maintenance Percentage (PMP) | Shows how much maintenance is planned instead of reacting to problems. |
By focusing on these numbers, you can lower repair costs and improve safety. Regular care also keeps machines working longer and avoids costly fixes.
Continuous improvement also inspires new ideas. When teams work together to improve care, they help the company succeed over time.
Tip: Start by tracking OEE and MTBF. Use this data to plan better maintenance steps.
Benefits of Total Productive Maintenance

Improved Equipment Reliability and Performance
Total productive maintenance helps machines work better and last longer. Fixing small problems early stops breakdowns and keeps equipment strong. Simple tasks like cleaning and oiling make machines run smoothly. This care reduces damage and improves how machines perform.
Companies using TPM often see big improvements in machine reliability. Machines break down less, so production stays steady. Better machines mean fewer delays and higher-quality products. Reliable equipment also helps meet deadlines and keeps customers happy.
Tip: Check machines regularly to find and fix problems early.
Reduced Downtime and Operational Costs
Downtime slows production and costs money. TPM reduces downtime by planning repairs before machines fail. This saves time and lowers expenses.
Here’s a table showing changes after using TPM:
TPM Aspect | Before TPM | After TPM | Cost Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
Downtime (hours/year) | 500 | 100 | 80% |
Repair Costs (USD/year) | 100,000 | 25,000 | 75% |
Spare Parts Inventory (USD) | 50,000 | 10,000 | 80% |
Energy Consumption (kWh/year) | 1,000,000 | 900,000 | 10% |
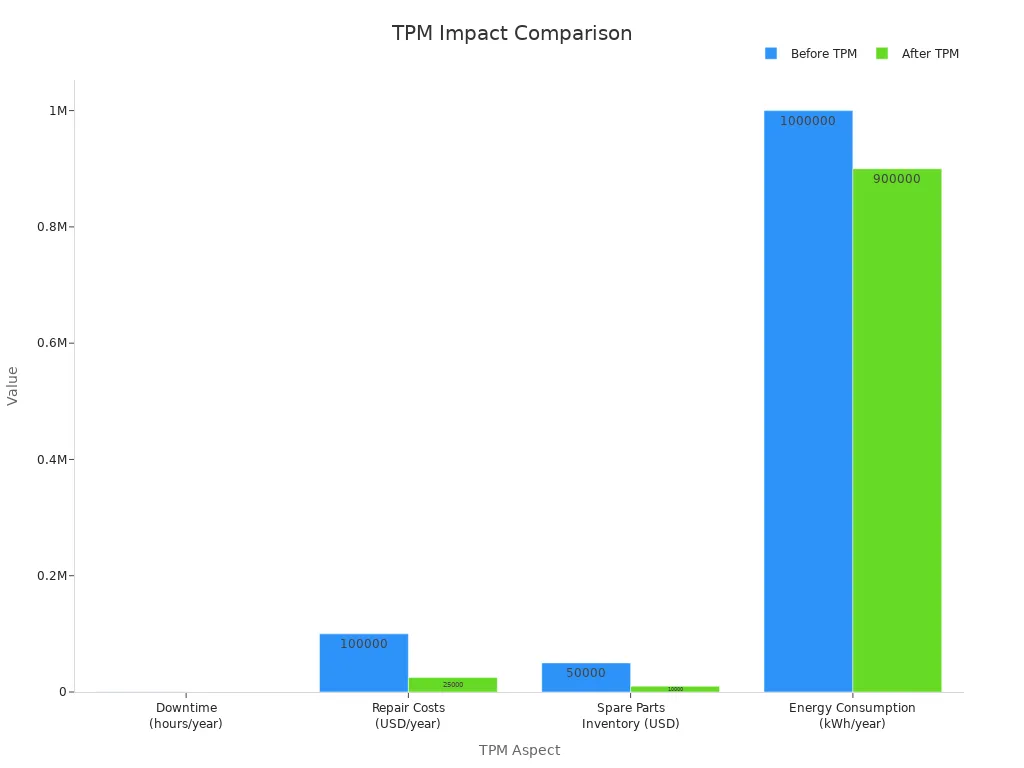
Less downtime means faster production and lower costs. This makes work more efficient and saves money.
Enhanced Employee Engagement and Safety
TPM builds teamwork and responsibility among workers. Employees help care for machines, which boosts confidence and teamwork. When workers feel involved, they help the company succeed.
TPM also makes workplaces safer. Workers clean and check their areas, reducing risks and accidents. For example, accidents dropped from 15 to 3 after starting TPM:
Safety Metric | Before TPM | After TPM |
|---|---|---|
Reported Accidents | 15 | 3 |
Involving workers in machine care improves safety and builds pride in their work. This leads to happier and more productive employees.
Note: Offer training programs to teach workers about safety and machine care.
Higher Productivity and Quality Standards
Total productive maintenance (TPM) helps boost productivity and keep quality high. By taking care of machines early and improving them often, equipment works better. This leads to smoother production and better results.
Using TPM reduces downtime a lot. Machines run longer without stopping, making work faster. For example, fixing small issues early keeps machines reliable. This avoids sudden breakdowns and helps meet deadlines on time.
Quality also gets better with TPM. Fixing problems early means fewer mistakes in products. Quality maintenance ensures machines work accurately, creating reliable results. This makes customers happy and improves your reputation.
Here’s a table showing how TPM helps productivity and quality:
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Less downtime means smoother and faster production. | |
Improved Quality | Better machine care leads to fewer product defects. |
Enhanced Compliance | TPM helps meet rules and stay competitive in the market. |
TPM also improves overall equipment effectiveness (OEE). This measures how well machines work in speed, quality, and uptime. Higher OEE means better productivity and success. The table below shows TPM's impact:
Improvement | Impact |
|---|---|
Equipment Reliability | Early care keeps machines running longer with fewer stops. |
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) | Better OEE means higher efficiency and smoother operations. |
By following these steps, you can improve productivity, keep quality high, and succeed long-term.
Tip: Check OEE often and fix small problems quickly to avoid bigger issues.
How to Implement Total Productive Maintenance
Step-by-Step Guide to TPM Implementation
Starting total productive maintenance (TPM) needs a clear plan. Follow these steps to create a strong TPM system:
Get Management Support: Leaders must back TPM fully. They should set goals and provide resources. For example, in Ethiopia’s malt industry, good leadership improved performance greatly.
Teach Employees: Train workers about TPM basics. Training helps them care for machines better. A study showed operator involvement grew from 14% to 37% after training, boosting machine performance.
Check Current Processes: Look at your maintenance system for weak spots. For instance, an auto parts company used equipment effectiveness to find and fix problems.
Start TPM Pillars Slowly: Begin with simple steps like cleaning and planned repairs. A polymer company raised equipment effectiveness from 75% to 85% by adding TPM pillars step by step.
Track Progress: Use tools like OEE to measure success. Tracking helps you see what works and where to improve.
Best Practices for Sustaining TPM
Keeping TPM running well takes effort. Use these tips to stay on track:
Promote Teamwork: Get all departments working together. In Egypt, teamwork helped raise OEE from 60% to 73.1% in 15 months.
Do Regular Maintenance: Check and fix machines often to avoid breakdowns. This keeps machines reliable and reduces downtime.
Celebrate Wins: Reward progress to keep workers motivated. Highlighting better machine performance keeps everyone engaged.
Update Training: Teach workers new skills regularly. This ensures they stay good at maintaining machines.
Overcoming Common Challenges in TPM Adoption
Starting TPM can be hard, but knowing the problems helps you solve them:
Lack of Clear Plans: Workers may not know their roles. Set clear goals and explain tasks to guide them.
Limited Budgets: Small budgets can slow progress. Begin with small changes and grow as results improve.
Fear of Change: Workers may resist new ideas. Train them and include them in decisions to build trust.
A study using the DEMATEL method showed that setting goals and training workers are key to success. These steps improved performance, proving challenges can be solved with the right actions.
Tip: Review your TPM plan often to fix problems early.
FAQ
What is the first step to start Total Productive Maintenance?
Start by getting full support from your leaders. They should set clear goals and provide resources. This helps everyone understand TPM's value and work together to apply it.
How often should you perform maintenance checks?
Do maintenance checks often, based on equipment use. Weekly or monthly checks work well for most industries. Regular checks catch small problems early and stop big breakdowns.
Can small businesses benefit from TPM?
Yes, small businesses can gain a lot from TPM. It cuts downtime, makes machines more reliable, and lowers repair costs. Even with fewer resources, simple steps like cleaning and planned fixes help a lot.
How does TPM improve workplace safety?
TPM gets workers to clean and check machines often. This lowers risks of accidents or machine failures. A safer workplace makes workers feel confident and keeps things running smoothly.
Is training necessary for TPM?
Yes, training is very important. It teaches workers how to care for machines. Skilled workers can spot and fix small problems, keeping machines running better and avoiding delays.
Tip: Begin with easy training sessions for basic care tasks. Add more as your team learns and grows.
See Also
Understanding Functional Testing In CNC And Die Casting
Exploring Dispensers: Their Role And Function In Manufacturing
A Supplier's Guide To CBAM And Sustainable Casting Practices
Top 10 Surface Finishing Techniques Every Metalworker Should Know
The Impact Of Thermal Management On EV Battery Longevity
About Hunan Puka
Established in 2016 and based in Hunan, China, with a liaison point in Berlin, we are a Tier 2 supplier for the automobile industry. We specialize in the production of customized aluminum die-casting parts designed for machines with a closing force ranging from 280 to 1250 tons, with subsequent manufacturing process CNC machining and surface treatment. Our commitment to quality is reflected in our accredited quality management system, certified by ISO9001:2015 and IATF16949:2016 standards.


