Step-by-Step Guide to Implementing a Quality Control Circle in Your Organization

A quality control circle is a small group of workers. They meet often to fix quality problems. You are important in this process. Your team leads the way to make things better. When your team acts as a quality circle, you help make products better. You also help save money and make customers happy. Many companies use this method to give teams more power. It also helps people talk openly. Picture your team finding the same problem on the line again and again. By using a quality control circle, your team can study the problem. Your team can share ideas to fix it and check if things get better. This guide helps your team do well with quality and teamwork at each step.
What Is a Quality Control Circle

A quality control circle is a small group of workers. They meet often to talk about problems at work. You and your team use this way to make things better. This idea started in Japan. Teams had ten or fewer people and a supervisor. They worked on making things better and learning new skills. Many businesses use quality circles. They help everyone join in quality management. When you join, you help make a place where people want to improve things.
Core Principles
Teamwork is very important in a quality circle. People talk openly and try to always get better. The PDCA cycle helps your group fix problems. First, you plan what to do. Then, you try it out. Next, you check if it worked. Last, you act on what you learned. This cycle helps you keep making things better. You use tools like Statistical Process Control to watch data and find problems early. Six Sigma and Total Quality Management help you measure and improve quality. For example, the Toyota Production System uses these ideas to save time and work better. In factories, quality circles help you find out why mistakes happen. Then, you fix them for better products and smoother work.
Key Benefits
When you join a quality circle, you get many good things.
You help stop mistakes. One study showed a quality circle made coding errors go down from 7.02% in many cases.
You learn new skills. People in quality circles got better at solving problems, talking, working together, and being responsible.
You see good changes. One review showed a quality circle made work and team skills better by 61.8%.
You help your workplace. Quality circles make work better, help people share ideas, and get more done.
You become a better leader. By joining, you learn to lead and work with all kinds of people.
Tip: Quality circles help you feel more excited and happy at work. You learn new things, fix problems, and make your job better for everyone.
Plan for Implementation
Assess Readiness
Before you start a quality control circle, you need to check if your organization is ready. You can use surveys like the Organizational Readiness to Change Assessment (ORCA) to measure this. ORCA uses numbers and scales to show how prepared your team feels. It checks if people want to join the process and if they have the right support. You can also use the Inventory of Factors Affecting Successful Implementation and Sustainment (IFASIS). This tool asks your team to rate how important different things are and how well your organization does them. High scores mean your team is ready for the process. These tools help you find strengths and spot problems before you begin. When you use these surveys, you get real data to guide your next steps. You can see if you need more training or better communication. This makes the process smoother and helps you avoid surprises.
Tip: Use team meetings to talk about survey results. Let everyone share ideas about what helps or blocks the process.
Set Objectives
Clear goals help your quality control circle stay focused. You should set objectives that match your team's needs and the organization's vision. Lean principles and Six Sigma tools help you find waste and improve the process. Total Quality Management (TQM) brings everyone into the process and keeps quality at the center. You can use the PDCA cycle to guide your work:
Plan: Find a problem, set a goal, and make a plan.
Do: Try your plan on a small part of the process.
Check: Look at the results and compare them to your goal.
Act: Keep what works or change your plan to improve the process.
You can also use tools like brainstorming, mind maps, and cause & effect diagrams. These help you see the process clearly and find the best way to reach your goals. When you use data and teamwork, you make the process stronger and more effective.
Note: Good objectives use real data and focus on making the process better for everyone.
Start a Quality Control Circle
Starting a quality circle helps your workplace get better. You need the right people and clear jobs for everyone. This part shows you each step so your team can use the quality control circle well.
Form a Steering Committee
First, make a steering committee. This group leads the quality circle program and helps all teams. Ask people from different departments to join. When you have people from many areas, you get more ideas. You also find better answers. It is important for leaders to help. Managers should join or support the group. This tells everyone that quality is important.
The steering committee makes the rules for the quality circle. They help teams pick projects and give them what they need. They also fix problems and check how things are going. They share results with the bosses. Big companies like Toyota Motors and Tata Steel use steering committees. These companies show that strong leaders and teamwork help make things better for a long time.
Tip: A steering committee with people from production, maintenance, and quality management brings many skills and makes your team stronger.
Select Members and Facilitators
Now, pick members and facilitators for each quality circle. Ask people who want to help and fix problems. People who choose to join work harder and care more. You can make circles by department, shift, or type of job. This helps the team work on real problems in their area.
Pick a facilitator for each quality circle. The facilitator helps the team stay focused and learn new things. The team can pick their own leader, or a manager can be the leader if the team agrees. The facilitator connects the team and the steering committee. They set up meetings, give training, and help with feedback. At companies like Xerox and Canon Inc., facilitators help the quality circle work well.
Here are some good ways to pick members and facilitators:
Ask for volunteers to join the quality circle.
Let the team pick their leader.
Give each team a trained facilitator.
Make circles by shared work or department.
Decide things like the circle’s name as a group.
Note: A good facilitator helps the team, gives training, and makes sure everyone can share ideas.
Define Roles
Clear jobs help your quality circle work better. Each person has something to do. The leader runs meetings and keeps the team working. The facilitator helps the leader and gives training. One person is the recorder and writes down what happens. Other members share ideas and help fix problems.
A big survey of factories found that sharing quality circle stories inside and outside the company brings more new products and better results. When you give everyone a job and let them share, your team can make real changes. The bosses should help the quality circle by giving feedback and saying “good job.” This keeps the team working hard and caring about quality.
Role | Main Task | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
Leader | Runs meetings, keeps team on track | Guides the process |
Facilitator | Supports team, provides training | Keeps quality circle effective |
Recorder | Takes notes, tracks progress | Documents improvements |
Member | Shares ideas, solves problems | Drives quality improvement |
Management | Gives support, reviews results | Ensures lasting success |
Callout: When everyone knows their job, your quality circle can fix problems faster and make things better for everyone.
Many companies, like IBM, show that clear jobs and strong support from bosses help quality circles do well. Your team can use these steps to build a quality circle that makes things better, helps teamwork, and supports your goals.
Train and Organize
Provide Training
Your team needs good training to do well. Training helps everyone find problems and make things better. You can use charts, pictures, and practice to learn. For example, you can make charts that show each step. This way, everyone knows what to do and who does it. Using pictures and hands-on practice helps you use tools the right way. When you practice a lot and check your skills, you get better at following rules. Training also helps you talk and solve problems together. You learn to share ideas and fix things as a team. This means you make fewer mistakes and do better work.
Training Methodology Component | Description | Performance Outcome |
|---|---|---|
Structured Workflows | Charts and clear steps for each task | Lower failure rates and better quality |
Diagrams and Practice | Visual guides and hands-on training | Fewer mistakes and better cleaning quality |
Regular Assessment | Monthly checks and feedback | Higher skill and better quality results |
Active Communication | Team talks and problem-solving sessions | Stronger teamwork and more professional growth |
Tip: Training helps your team care about quality and be ready for new things.
Establish Structure
A strong setup helps your team work well. You should make sure everyone has a clear job. The best team size is 6 to 12 people. Your group should have a leader, members from different jobs, and a quality expert. This gives you many ideas and skills. If your team can make some choices on its own, you can try new things. When jobs are clear, everyone knows what to do. The leader runs meetings, members help fix problems, and the expert gives advice. You also need help from top bosses. They give feedback and check how things are going. Real data shows that a good setup can cut mistakes by 25% and make people 30% happier.
Set Meeting Guidelines
Meetings are very important for your team. You should meet every month with 5 to 10 people. Each person has a job, like leading, writing notes, or sharing news. In meetings, you share ideas, look at facts, and make choices. Good meetings help you talk, decide, and act. Bad meetings slow down your work. You should write down what happens in each meeting and follow a 6-month plan for your projects. Use tools like fishbone diagrams and the 80/20 rule to find and fix problems. When you keep track of your work and share what you learn, your team gets better over time.
Meeting Guideline Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Meeting Frequency | Hold meetings twice a month |
Member Roles | Assign tasks and report progress |
Topic Selection | Brainstorm, score, and vote on topics |
Problem Investigation | Collect data and use inspection forms |
Root Cause Analysis | Use diagrams and group scoring |
Countermeasure Development | Discuss and score solutions |
Outcome Measured | Track reduction in failure rates |
Note: Having regular, good meetings helps your team reach its goals and keep getting better.
Operate the Quality Circle
Run Meetings
You help your quality circle by having meetings with clear goals. Start each meeting by looking at your goals. Check what you have done and talk about problems. Clear goals help your team stay on track. When everyone joins in, your group works better together. Use a simple plan to run the meeting. Give jobs like leader, note-taker, and timekeeper to team members. Ask everyone to share ideas and listen to others. Training and using the right tools make meetings work well. Rewards and feedback help your team stay excited. Good meetings help people be creative and take action. You also build trust and help people feel responsible. Taking good notes and giving feedback help your team see how they are doing and keep getting better.
Tip: After every meeting, use a report and feedback to help your team keep improving.
Use Problem-Solving Tools
You need the right tools to fix problems and make things better. Start with Check Sheets to write down problems or mistakes. Use Scatter Diagrams to see if two things are connected, like training and product quality. These tools help you find patterns and make smart choices. DMAIC is a step-by-step way to solve problems from start to finish. You can also use Fishbone Diagrams to find main causes, Control Charts to watch for changes, and Value Stream Mapping to find waste. Kaizen helps you make small changes that add up over time. These tools help you make fewer mistakes and better products. When you use them, your process gets stronger and more dependable.
Use Check Sheets to collect data.
Try Scatter Diagrams to see cause and effect.
Use DMAIC to solve problems step by step.
Use Fishbone Diagrams and Control Charts to look deeper.
Implement Solutions
After you find the main cause, your team makes and tests new ideas. Pick ideas that fit your goals and help quality. Watch your progress using key performance indicators (KPIs). KPIs show how well your ideas work and where you can do better.
Description | |
|---|---|
Non-Conformities | Products or services that do not meet standards |
Number of Complaints | Customer complaints in a set time |
On-Time Delivery | Orders delivered within the promised time |
Percentage of Conformance | Outputs that meet quality standards |
Percentage of Defective Products | Products that fail quality checks |
Process Capability (CPK) | How well your process meets quality limits |
Product Reliability | How long a product works as expected |
Quality Cost Ratio | Cost of quality efforts vs. cost of poor quality |
Rework Rate | Units that need fixing after production |
Scrap Rate | Materials or products thrown away |
You can also use First Pass Yield and Customer Satisfaction Index to see if your ideas help quality and speed. Set clear goals, collect data, and check results with your team. If an idea does not work, change your plan and try again. This way, you keep making your work better and reach higher quality.
Note: Always cheer for small wins and share results with your team to keep everyone interested.
Measure Improvement

Track Progress
You need to track progress to see if your quality control circle works. The Plan–Do–Study–Act (PDSA) cycle is a strong way to follow your improvement steps. You plan a change, do it, study the results, and act on what you learn. Many teams use this cycle to check if their quality efforts bring real improvement. Some studies show big gains in quality and performance when teams use PDSA the right way. Other studies find no change, which means you must use the cycle carefully and match it to your team’s needs. You can use charts and checklists to record each step. This helps you see if your process is moving forward and if your team’s actions lead to better quality. When you track progress, you spot problems early and keep your team focused on improvement.
Tip: Write down each step of your process and review it often. This keeps your quality goals clear and your team on track.
Review Results
You must review results to know if your quality circle made a difference. Use simple tools to look at your data. Many teams use the Pareto principle, fishbone diagrams, flow charts, and checklists to study quality problems. These tools help you find the main causes of issues and measure how much you improved. You can also use tables to compare defect rates before and after your quality circle started. Some teams use radar maps to show how team skills and group work improved. To check if your changes matter, look at achievement rates and improvement rates. These numbers show how much your quality and performance grew. Teams often use software like SPSS to run tests and see if the results are real. When you review results, you learn what worked and what needs more work. This helps you keep building quality and efficiency in your process.
Tool or Report | What It Shows | Why Use It? |
|---|---|---|
Pareto Chart | Main causes of quality problems | Focus on biggest issues |
Fishbone Diagram | Root causes of defects | Find what to fix first |
Flow Chart | Steps in the process | Spot weak points |
Checklist | Tasks completed | Track quality actions |
Achievement Rate | Goals reached | Measure performance |
Improvement Rate | Change over time | See quality growth |
Note: Regular reviews help you keep your quality circle strong and your performance high.
Overcome Challenges
Address Resistance
When you start a quality control circle, some people may not like it. Some team members might worry about doing more work. Others may feel nervous about trying new things. Not having enough time or feeling unmotivated can slow things down. You can fix these problems with help from leaders and by talking clearly.
Japanese and American companies that use Japanese quality management methods get more workers involved. They also see better results. These companies let workers have more responsibility and use easy quality tools. This way, people do not fight change as much and quality circles work better.
Leaders should share quality jobs with workers and give them the right tools. When you feel trusted and have what you need, you want to help make things better.
Studies show teams with strong friendships, clear goals, and good leaders have less trouble. Leaders who care and listen help teams feel excited to join in.
A seven-step plan helps leaders use your skills to make things better. This plan helps people work better, make higher quality products, and enjoy their jobs more.
Tip: Leaders should let you help make choices and be part of decisions. When you help shape the process, you feel more interested and less likely to say no.
Sustain Engagement
It takes work to keep your team interested in quality circles. You need support, training, and praise to stay excited. Many companies do well by using these ideas:
Metric | Evidence / Result | Example / Impact |
|---|---|---|
Productivity Increase | 15% more work done after starting quality circles | A factory made more products by fixing steps and cutting waste |
Error Rate Reduction | 30% fewer coding mistakes because of team reviews and working together | An IT company made better software with fewer errors |
Employee Engagement | 20% higher employee happiness after using quality circles | Surveys showed people liked their jobs more and felt they mattered |
Customer Satisfaction | 10 points higher on customer happiness after quality circles worked on shopping | A store got better feedback and happier shoppers |
Financial Performance | 5% more profit after one year of using quality circles | Saving money, selling more, and making fewer mistakes helped the company earn more |
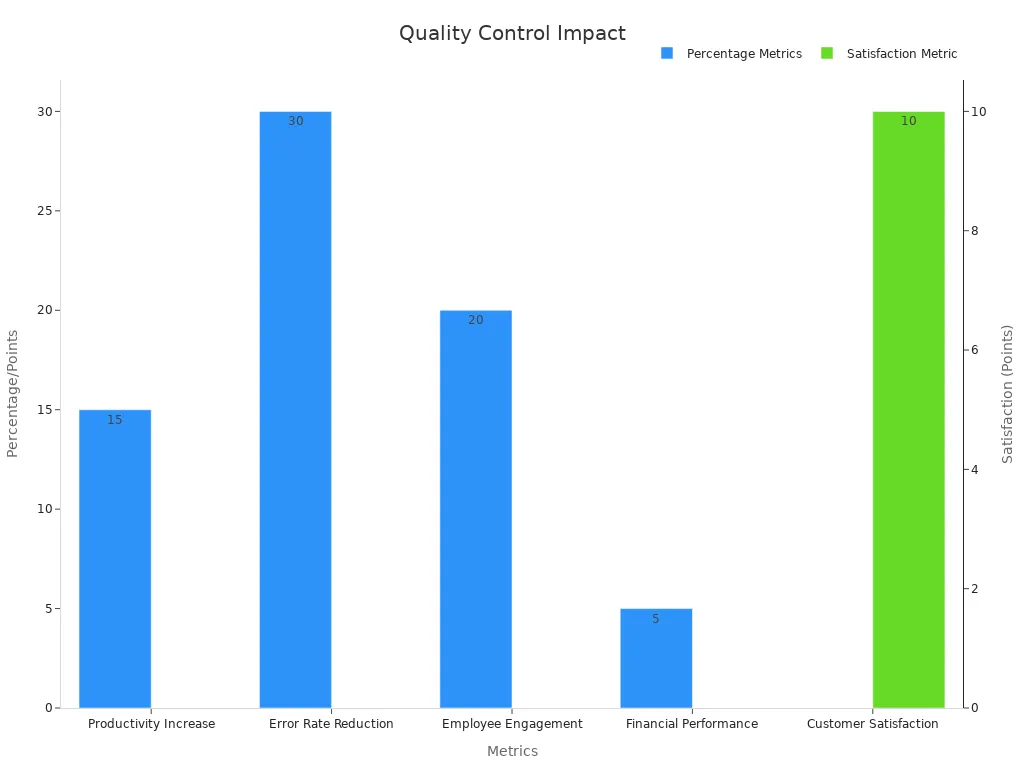
You can keep people interested by:
Letting everyone help make choices, so they feel safe and important.
Making sure leaders give what is needed and know why quality circles help.
Giving training so everyone feels ready to fix problems and share ideas.
Having regular meetings and talking clearly to stop confusion.
Cheering for small wins and setting short goals to keep everyone moving forward.
When you use these ideas, your team stays focused on getting better. Support from leaders, good training, and open talks help quality circles last and do well.
Share Success
Real-World Examples
Quality control circles are used in many countries. In Japan, there were over one million circles by 1978. More than ten million workers joined these groups. This shows that companies trust this way of working. Many places saw workers get more involved and fix problems faster. Teams found issues and solved them quickly. This helped them use better solutions and keep getting better.
Here is a table with some real-world examples:
Aspect | Description / Example |
|---|---|
Historical Growth | Over one million circles in Japan by 1978, with ten million workers involved |
Organizational Benefits | More engaged workers, faster problem solving, better solution follow-through |
Key Metrics | Faster solution times, cost savings, higher quality, more projects finished |
Six Sigma Integration | Circles help with Six Sigma steps and act as early warning teams |
Industry Examples | Lockheed Martin (USA), European companies, healthcare, and service sectors |
Measurable Outcomes | Lower costs, better product quality, higher morale, and stronger team performance |
These examples show how quality circles help teams do better and reach their goals.
Best Practices
You can use these best practices to make your quality circle strong:
Use clear methods like Six Sigma, Total Quality Management, Lean Manufacturing, and Statistical Process Control. These give you steps to follow and results you can measure.
Let all workers join your quality circle. When everyone joins, you get better ideas and more ways to improve.
Watch important numbers like defect rates, first-pass yield, scrap rates, and customer complaints. These numbers help you know where to work harder.
Use tools like control charts and root cause analysis. These tools help you find problems early and fix them before they get bigger.
Give training and support from leaders. Good training and help from leaders keep your team working well and improving.
Mix different quality methods to fit your business. Check your progress often and use technology to help your team do better.
Tip: If you use these best practices, your team can fix problems faster and keep quality high.
You can help your workplace get better by starting a quality control circle. Start with easy steps and let your team learn together. After a while, you will notice many good things:
You help your company spend less money and waste less.
You make teamwork stronger and finish projects better.
You make customers happier and want to come back.
You help products and services get better.
You help your company stay strong against others.
Keep learning new things and trying to improve. Quality control circles will help your organization do well in the future.
FAQ
What is the main goal of a quality control circle?
You use a quality control circle to find and fix problems at work. Your team works together to improve quality. You help your company make better products and services.
How often should your team meet?
You should meet at least once or twice a month. Regular meetings help you track progress and solve problems quickly. Your team stays focused and motivated.
Who can join a quality control circle?
Anyone in your workplace can join. You can invite people from different departments. This brings new ideas and helps your team find better solutions.
What tools do you use in a quality control circle?
You use check sheets, fishbone diagrams, and control charts. These tools help you find problems, track progress, and measure results. Your team can choose the best tool for each task.
See Also
Why QRQC Is Crucial For Today’s Quality Management
Helpful Tips For Choosing Measurement Instruments In QC
Understanding PPAP As A Vital Manufacturing Quality Tool
A Clear Guide To Acceptable Quality Limits In QC
How Statistical Process Control Improves Manufacturing Results
About Hunan Puka
Established in 2016 and based in Hunan, China, with a liaison point in Berlin, we are a Tier 2 supplier for the automobile industry. We specialize in the production of customized aluminum die-casting parts designed for machines with a closing force ranging from 280 to 1250 tons, with subsequent manufacturing process CNC machining and surface treatment. Our commitment to quality is reflected in our accredited quality management system, certified by ISO9001:2015 and IATF16949:2016 standards.


