What Are the Key Principles of Lean Manufacturing

Lean manufacturing key principles help companies get more value and cut waste. Almost 70% of U.S. factories use lean manufacturing. They got the idea from the Toyota Production System. The five principles of lean manufacturing are:
Identify value by seeing what matters to the customer.
Map the value stream to find all steps and waste.
Create flow so value moves easily to the customer.
Establish pull so production fits what customers want.
Seek perfection by always trying to improve.
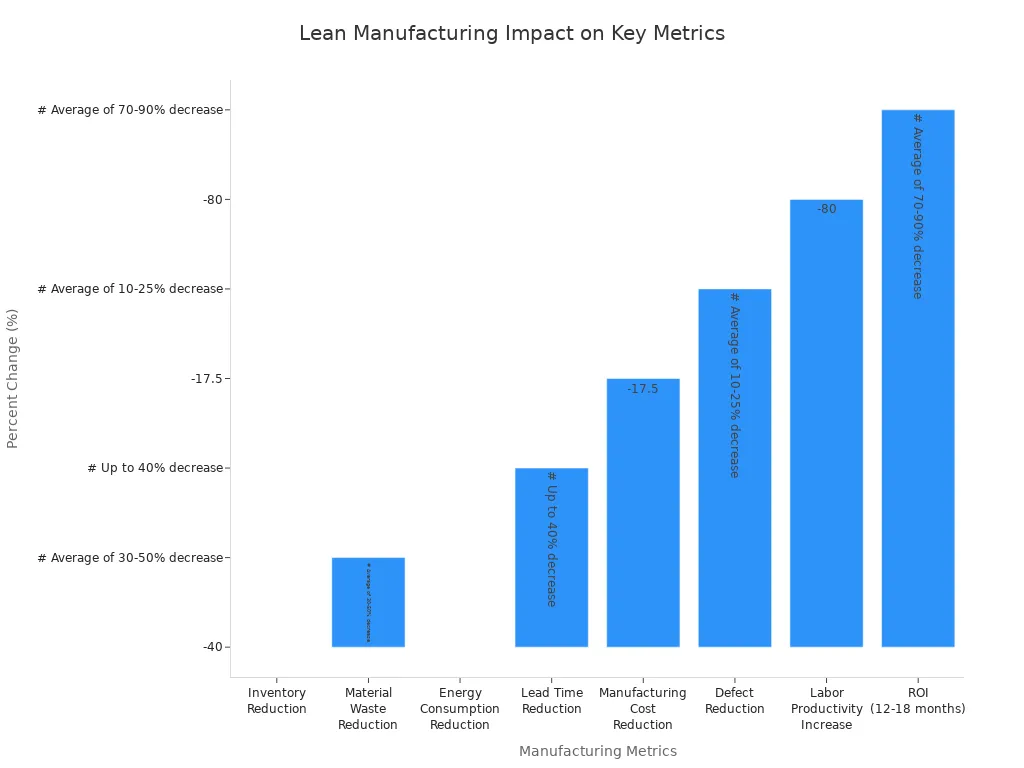
Lean manufacturing principles help make better products and give customers more value. They do this by focusing on what is most important. Tools like Kanban and Kaizen, plus teamwork, support these main ideas. The table below shows how lean cuts waste and makes quality better:
Metric | Impact of Lean Manufacturing |
|---|---|
Inventory Reduction | |
Material Waste Reduction | Up to 40% decrease |
Energy Consumption Reduction | 10-25% decrease |
Lead Time Reduction | 70-90% decrease |
Manufacturing Cost Reduction | 25-30% decrease |
Defect Reduction | 80% decrease |
Labor Productivity Increase | 35% increase |
Return on Investment (ROI) | 200% average ROI within 12-18 months |
Lean Manufacturing Key Principles

The five main ideas of lean manufacturing help cut waste and make quality better in factories. These important ideas—Value, Value Stream, Flow, Pull, and Perfection—help companies focus on what customers want most and keep making things better.
Value
Value is the most important part of lean manufacturing key principles. It means what the customer really wants and will pay for, like good quality, special features, or fast shipping. Lean manufacturing starts by finding out what is important to the customer. This means learning about the product’s job and how happy it makes the customer.
Manufacturers use different ways to measure value:
They look at sales numbers and watch what customers do.
They use tools like Critical To Quality (CTQ) and Quality Function Deployment (QFD) to turn customer needs into technical details.
For example, a company might learn that customers care more about fast shipping than extra features. By focusing on what customers want, lean manufacturing makes sure every step adds value and skips steps that waste time. Tools that show real-time data help companies match their work to what customers want, so value is easy to see and use.
Tip: Companies that care more about value than just the product can help customers more and make them happier.
Value Stream
The value stream is all the steps—both helpful and not—that move a product from raw material to the customer. Drawing a map of the value stream is a big part of lean. It helps teams see every step, from the supplier to the customer, and find where waste happens.
Value stream mapping uses special symbols to show how things and information move. The steps usually are:
Draw a map of how things work now.
Make a new map that removes waste and makes things flow better.
Write a plan to go from the old way to the new way.
Description | |
|---|---|
Overproduction | Making too much, which means more storage and longer waits. |
Waiting | Time when nothing is happening to the goods. |
Transport | Moving goods when it is not needed. |
Over-Processing | Doing extra work that does not help. |
Excess Inventory | Having too much stock, which costs more and hides problems. |
Unnecessary Motion | Workers moving too much, which slows things down and can be unsafe. |
Defects | Mistakes that need fixing or cause waste. |
Mapping the value stream lets teams see the whole process, not just one part. This helps them find and remove waste, talk better, and keep improving.
Flow
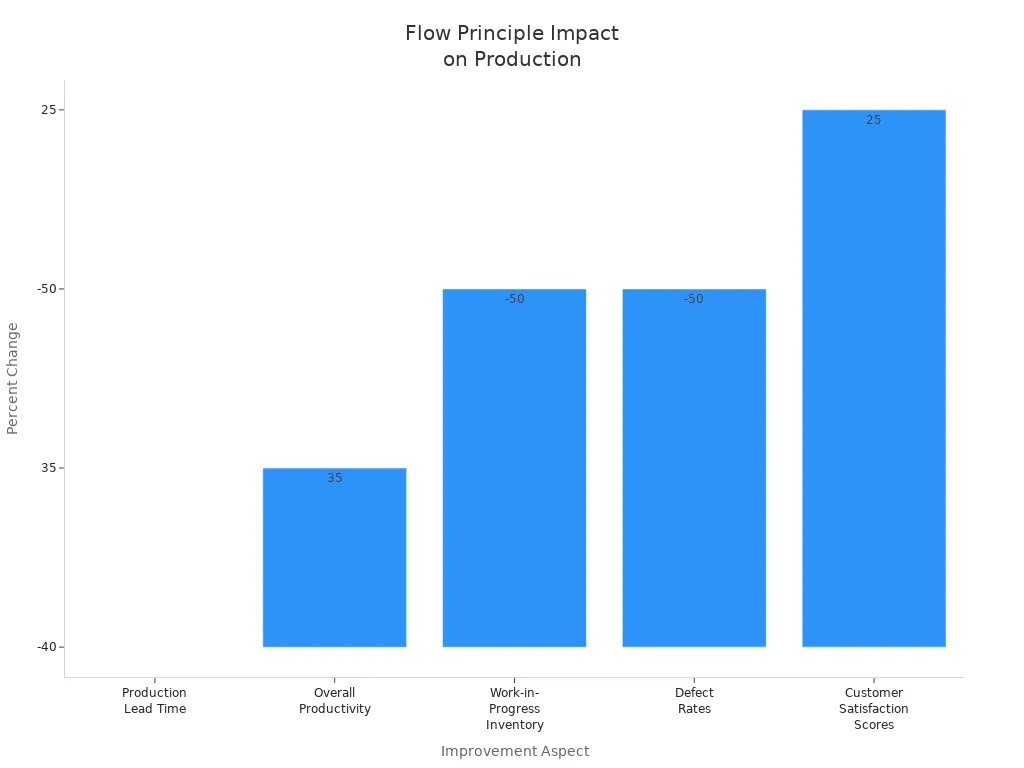
Making flow means work moves smoothly from one step to the next without stopping. This lean manufacturing idea is about setting up work areas, making layouts better, and putting tasks in the right order. When companies make flow, they cut waiting, lower inventory, and make quality better.
The flow idea gives many good results:
More work done (up to 35% more).
Less unfinished work (up to 50% less).
Fewer mistakes (up to 50% less).
Happier customers (up to 25% more).
Problems with flow can be bottlenecks, uneven work, hard steps, and broken machines. Lean manufacturing fixes these by making steps easier, sharing work, and using digital tools for quick instructions. By working on flow, companies can give value faster and with better quality.
Pull
Pull is a main idea that makes lean manufacturing different from old ways. Instead of making things based on guesses, companies only make what the customer asks for. This way, called Just-in-Time (JIT), lowers inventory, cuts waste, and helps companies react to real needs.
Aspect | ||
|---|---|---|
Production Basis | Makes things based on guesses about demand | Makes things only when customers order (Just-in-Time) |
Keeps lots of inventory to meet guesses | Keeps little inventory, makes only what is needed | |
Waste and Efficiency | Can make too much and have extra inventory | Cuts waste by making only what is needed |
Responsiveness | Not flexible, slow to change | Very quick and ready for real demand |
Planning and Control | Central planning, makes schedules from guesses | Local control, makes things when needed |
Risk | Can have too much stock and pay more for storage | Might run out if demand jumps up fast |
Companies that use pull systems often see inventory drop by over 30% and lead times drop by 40%. For example, a company using Kanban cards to show what to make can cut unfinished work by almost half. Pull systems help companies stay lean, save money, and give customers what they want when they want it.
Perfection
Chasing perfection means never saying “good enough.” Lean manufacturing wants everyone to look for ways to make things better, cut waste, and raise quality. This idea is about always improving, or Kaizen, where small changes add up to big results.
Continuous improvement means:
Checking processes often and asking workers for ideas.
Using tools like 5S, Total Productive Maintenance (TPM), and the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle.
Watching important numbers like cycle time, mistakes, and lead times.
Note: Perfection is something you keep working toward. Companies like Toyota and Boeing have made big gains by letting workers share ideas and by making small, steady changes.
Company | Lean Tools Implemented | Key Improvements Achieved |
|---|---|---|
Just-in-Time, 5S, Suggestion System | Less waste, faster work, high quality, happy customers | |
Boeing | Lean, Six Sigma, Kaizen, JIT | 30% less time to make things, 50% fewer mistakes, better quality |
Virginia Mason Medical Center | 5S, root cause analysis, Kaizen events | 40% shorter wait times for patients, happier patients |
Walmart | JIT, Six Sigma, Kaizen, analytics | Saved money, quick supply chain, better inventory control |
By working toward perfection, companies build a culture of new ideas and change. They use lean manufacturing key principles to keep making quality, efficiency, and customer value better.
Applying Lean Principles
Lean Tools
Lean manufacturing uses many helpful tools to support its main ideas. These tools help teams find waste, remove it, and make work better. They also help work move smoothly and improve quality. Some of the most common lean tools are:
Kanban: Teams use cards to show what work needs to be done. These cards help limit how much work is happening at once. This tool helps teams see problems and keeps work moving. For example, a CNC shop had fewer tool shortages after using Kanban cards.
5 Whys: Teams ask “why” five times to find the real cause of a problem. This method helps fix problems at their source. It leads to better quality and less waste.
Kaizen: Workers share small ideas for change every day. These small changes add up to big improvements in how things work.
5S System: Teams keep work areas neat and safe. This helps people find things faster and work better. A medical device plant found parts faster after using 5S.
SMED: This tool helps teams switch between products quickly. It cuts setup time and helps reduce waste.
Poka-Yoke: Special devices stop mistakes before they happen. This helps make quality better.
Lean tools like these help companies lower inventory, cut mistakes, and save time. They also help teams work better and faster.
Continuous Improvement
Continuous improvement is a big part of lean manufacturing. Teams work together to make small changes all the time. These changes help make quality better and waste less. Kaizen means “change for the better.” It asks everyone to look for ways to improve each day. Companies that use continuous improvement set clear goals and train workers. They also check progress with numbers like cycle time and mistakes.
Manufacturers have seen good results from continuous improvement. For example, Boeing had fewer mistakes after three years. Toyota checks quality every day to keep getting better. Digital tools help teams see problems fast and fix them quickly. These efforts help teams work faster, make fewer mistakes, and improve how things are done.
Tip: To keep continuous improvement going, make it part of daily work. Give workers the tools and help they need.
Respect for People
Respect for people is a key part of lean manufacturing. Leaders show respect by listening to workers and trusting their skills. They also ask workers to help solve problems. Managers spend time on the shop floor to see real work and hear ideas. When workers help plan their own work, they feel more involved and excited.
A culture of respect helps teams work better together. It also makes people happier at work and helps the company do better. Studies show that fair treatment and trust help workers join in and share ideas. Companies with happy workers do better, stay safer, and keep more workers. At Toyota, leaders look for answers that help everyone and show respect to all team members.
When leaders respect workers, they build trust. This helps create a place where improvement and quality can grow.
Benefits of Lean Manufacturing

Efficiency
Lean manufacturing helps companies work better by focusing on what adds value and cutting out waste. Teams use tools like the Taguchi method and Design of Experiments to make work faster and more steady. For example, car companies make cars faster and with better quality by changing how they put them together. Electronics makers have fewer mistakes by changing how they do things. Food companies make products more the same and waste less by finding the best ways to mix and cook.
Some ways to measure how much better things get are:
Costs go down
Products are higher quality
Machines work better (OEE)
Time is saved
Customers are happier
Companies make more money (ROI)
Workers are happier
Metric | Description |
|---|---|
How much product is made in a certain time. | |
Capacity Utilization | How much of the total possible output is being used. |
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) | Checks if machines are working well, fast, and making good products. |
Production Attainment | How often the company meets its production goals. |
Lean ways help companies work better, make more, and get better results.
Waste Reduction
Lean manufacturing tries to get rid of waste everywhere. By drawing maps of the value stream and using digital tools, teams can find and remove steps that do not help. Companies use lean ideas to cut waste, looking at the main seven wastes and also wasted talent. These wastes are overproduction, waiting, transportation, inventory, motion, overprocessing, and defects.
Waste Type | Description | Lean Manufacturing Reduction Approach |
|---|---|---|
Overproduction | Making more than needed, which means too much inventory. | Make only what is needed using just-in-time and real-time checks. |
Waiting | Time when nothing is happening because of delays. | Make schedules better and plan work together. |
Transportation | Moving things when it is not needed. | Change layouts and use pull systems. |
Inventory | Having too much stock, which uses up money. | Use just-in-time delivery and keep track of stock. |
Motion | Workers moving more than they need to. | Make work areas better and change how work is done. |
Overprocessing | Doing more work than needed. | Make steps the same and use tools to stop mistakes. |
Defects | Products that do not meet quality rules. | Build quality into each step and find the real cause of problems. |
Lean manufacturing helps companies cut a lot of waste, use resources better, and keep getting better.
Customer Value
Lean manufacturing gives customers more value by making work smoother and giving better products faster. Companies spend less on inventory and fill orders quicker after using lean. Product quality gets better, and customers get good service. For example, a store spent 20% less on inventory and sent orders 15% faster with lean. An online store fixed a 15% drop in customer happiness by making work better.
The main ways customers benefit are:
Products are better and more reliable
Orders arrive faster
Costs are lower because waste is gone
Customers are happier and stay loyal
Companies can change plans more easily
Companies that use lean ideas earn trust from customers and become stronger than others.
Lean manufacturing is based on five main ideas: value, value stream, flow, pull, and perfection. These ideas help companies waste less and give customers more value. To do well with lean, workers need to learn new skills and think in a lean way. Using tools like Kanban and Kaizen is also very important.
Experts say to start lean with good leaders, clear plans, and training that never stops. Lean works best when teams check how they are doing, cheer for small wins, and always try to get better. Companies that use lean let everyone help make changes and work toward big, lasting results.
FAQ
What is the main goal of Lean Manufacturing?
Lean Manufacturing tries to give customers more value. It does this by taking away waste from how things are made. Companies work to make products better and faster. They also try to use less time and fewer materials.
How does Lean Manufacturing reduce costs?
Lean helps teams find waste, like too much inventory or waiting. When teams remove waste, it costs less to make things. This helps companies save money and make more profit.
Can small businesses use Lean Manufacturing?
Small businesses can use Lean principles too. They can begin with easy tools like 5S or Kanban. These tools help teams keep work neat and get more done.
What are some common Lean tools?
Tool | Purpose |
|---|---|
Helps control workflow | |
5S | Keeps work areas tidy |
Kaizen | Helps teams improve daily |
5 Whys | Finds out why problems happen |
Lean tools help teams fix problems and keep getting better.
See Also
Boosting Engineering And Manufacturing Efficiency With Quick Response Methods
Understanding QFD FMEA And DOE Impact On Manufacturing Quality
Why QRQC Is Vital For Effective Modern Quality Control
The Importance Of APQP In Automotive And Aviation Industries
How To Successfully Implement A Quality Control Circle Step-By-Step
About Hunan Puka
Established in 2016 and based in Hunan, China, with a liaison point in Berlin, we are a Tier 2 supplier for the automobile industry. We specialize in the production of customized aluminum die-casting parts designed for machines with a closing force ranging from 280 to 1250 tons, with subsequent manufacturing process CNC machining and surface treatment. Our commitment to quality is reflected in our accredited quality management system, certified by ISO9001:2015 and IATF16949:2016 standards.


