How Net Shape Is Achieved in Die Casting

Net shape in die casting means parts come out of the mold ready to use. They already have the right shape and size. You do not need to cut or change them more. This helps save time and materials when making things. You get net shape in die casting by doing some important steps:
Design the part with CAD/CAM tools to match the final size.
Make molds and dies that are very exact for good metal flow.
Use special casting methods to stop shrinking and stress.
Make the cooling and ejection steps better to keep the right size and look.
Net shape in die casting is not the same as near net shape. Near net shape sometimes needs a little more cutting or shaping. Good accuracy, smart mold design, and digital modeling help make net shape work. These things also help modern factories grow.
Net Shape in Die Casting
What Is Net Shape Casting
Net shape casting means you make a part that needs no extra work. The part comes out of the mold just the way you want it. It has the right size, shape, and features. The mold is designed so the metal fills every detail. You do not need to grind, drill, or trim the part. This saves time and materials. For example, if you make a gear with net shape casting, you can use it right away.
The metal you pick changes how you do net shape casting. Magnesium alloys need special care because they can oxidize fast. Factories use gases like sulfur dioxide to protect the metal. Aluminum alloys melt at higher temperatures, so you use cold chamber die casting. Zinc and magnesium alloys melt at lower temperatures, so hot chamber die casting works well. Each metal needs its own way to get the best net shape casting results.
Net Shape vs. Near Net Shape Casting
You may hear about near net shape casting and wonder how it is different. Net shape casting gives you a finished part from the mold. You do not need to machine or finish it. Near net shape casting gives you a part that is almost done. You still need to trim or drill it to get the final shape.
Let’s look at some real examples to see the difference:
Product Examples | Manufacturing Method | Industry/Application | Implications for Industry |
|---|---|---|---|
Auto parts, communication base station cooling components | Cold-chamber die casting | Automotive, Telecom | Makes large, light, thin-walled parts; helps with automation and saves money. |
USB connectors, laptop cases | Hot-chamber die casting | Electronics, 3C products | Good for small, precise parts; improves quality and saves time and materials. |
Pure copper rotors | Die casting (special case) | Electrical machinery | Short mold life because of high melting point; shows process problems for some materials. |
You use net shape casting when you want to skip extra steps and save money. Near net shape casting is good when you need a part close to the final shape but still need to make small changes. For example, you might use near net shape casting for a car engine block that needs holes drilled after casting. In electronics, net shape casting is used for small parts like USB connectors that are ready to use.
Both near net shape and net shape casting help you waste less and save time. Automation and smart factory tools make these processes better. Real-time mold temperature control keeps quality high and helps molds last longer.
Why Net Shape Parts Matter
Net shape casting is very important in automotive, aerospace, and electronics. These industries need strong, light, and complex parts that fit together well. Net shape in die casting lets you make these parts fast and with less waste.
In cars, net shape casting is used for gears, housings, and brackets. These parts must be strong and exact. In aerospace, you need light parts with complex shapes, like frames and stiffeners. Net shape casting helps you make these without extra work. Electronics companies use net shape casting for small, detailed parts like connectors and cases. These parts must be exact to fit in small devices.
Net shape casting gives you many benefits:
You use less material, so you save money.
You spend less time making each part.
You get parts that are very accurate and high quality.
You make less scrap and help the environment.
For example, using net shape casting for a control valve cage can save up to 22% in costs and cut weight by 10%. You also spend less time machining and save a lot of scrap each year. These savings are important in industries where every dollar and every gram matter.
Tip: Choosing net shape casting helps your company stay ahead by making better parts faster and for less money.
Net Shape Casting Process

Achieving net shape casting in die casting involves several important steps. Each step helps you create parts that match the final design with little or no extra work. Let’s look at each stage in the process.
Part Design
You start with part design. You use CAD software to create a digital model of the part. This model shows every detail, including size, shape, and features. You must think about how the metal will flow and cool. You should keep wall thickness uniform. This helps the part cool evenly and prevents warping or cracks. Add draft angles to make it easier to remove the part from the mold. Avoid sharp corners and complex shapes unless you need them. Simple designs help you get better results in net shape casting.
Tip: Use digital modeling tools to test your design before making the mold. Simulation software can show you how the metal will fill the mold and where problems might happen. This helps you fix issues early and improve manufacturability.
You should also plan for the parting line and make sure features like holes or threads are easy to cast. By thinking ahead, you reduce the need for extra machining later. This step is key for both net shape casting and near net shape casting.
Mold and Die Creation
Next, you move to mold and die creation. You use the digital model to guide the making of the mold. CNC machines and EDM tools cut the mold with high precision. The quality of the mold affects the final part. If the mold is not accurate, the part will not match the design.
Advanced mold making uses new technologies. For example, 3D printing can create complex mold shapes that were hard to make before. Special coatings and materials make molds last longer and give better surface finishes. You also design the gating and venting systems to control how the metal flows and how air escapes. Good mold design helps you avoid defects and makes net shape casting possible.
Note: Precision in mold making lets you reach tolerances as tight as ±0.05 mm. This level of accuracy is important for industries that need high-quality parts.
Metal Injection
After the mold is ready, you prepare the metal. You melt alloys like aluminum, magnesium, or zinc. You inject the molten metal into the mold at high pressure. This step fills every detail of the mold quickly. You must control the injection speed and pressure. If the pressure is too low, the mold does not fill all the way. If it is too high, you get flash or damage the mold.
You can use vacuum systems to remove air and reduce porosity. The right settings depend on the metal and the part design. For thin-walled or complex parts, you need fast injection to fill the mold before the metal cools. Careful control at this stage helps you achieve net shape casting and reduces the need for extra work later.
Solidification and Ejection
Once the metal fills the mold, it starts to cool and solidify. You must control the cooling rate to avoid defects like shrinkage or cracks. Some advanced methods, like Controlled Diffusion Solidification, help create a better metal structure and reduce problems like hot tearing. This is important for both net shape and near net shape manufacturing.
When the part is solid, you open the mold. Ejector pins push the part out. You must place these pins carefully. If you do not, the part can bend or get marks that affect its size and look. Good ejection keeps the part true to its net shape.
Remember: The way you cool and eject the part affects its final accuracy. Even small mistakes here can mean more finishing work later.
Minimal Finishing
The last step is minimal finishing. Because you designed the part and mold so well, you do not need much extra work. You might trim off small bits of metal, called flash, or clean the part. You do not need to machine surfaces, add threads, or cut features. The part comes out of the mold almost ready to use.
This is the main goal of net shape casting. You save time and money because you skip many finishing steps. You also waste less material. In near net shape casting, you might still need to drill holes or polish surfaces, but you do much less than with older casting processes.
By focusing on each step, you make sure your manufacturing process produces high-quality parts with little waste. Net shape casting and near net shape casting both help you reach these goals, but net shape casting gives you the most savings.
Technologies for Net Shape Parts

Advanced Mold Design
To get true net shape in die casting, you need advanced mold design. Today, you can use CAD and CAE software. These tools help you make a digital model of your mold. You can also run tests on the computer. This shows how molten metal will move and where stress might happen. You can fix problems before making the mold.
Modern mold shops use many high-tech methods. CNC machining makes molds with very tight fits. EDM shapes hard parts of the mold with great detail. Multi-axis milling and high-speed machines help make tricky surfaces. Rapid prototyping lets you try new mold ideas fast.
Technology | Description and Contribution to Net Shape Mold Design |
|---|---|
Help you design and make molds that fit well, even after shrinkage. | |
Rapid Prototyping | Lets you test new mold shapes quickly and handle tough designs. |
EDM | Makes exact shapes for mold parts that are hard to create. |
Laser Beam Machining | Makes the mold surface smoother and work better. |
Multi-Axis Milling | Helps you shape tricky surfaces for better net shape parts. |
These tools help you reach both net shape and near net shape goals.
Process Controls
You must control every step in die casting to get good net shape parts. Real-time controls use sensors to watch things like pressure, temperature, and how fast the mold fills. If something is wrong, you get an alert right away. This helps you fix problems before they cause bad parts.
Many factories use software with measurement tools. For example, Verisurf software checks parts during and after casting. You can find size or shape problems fast. Automated checks on CNC CMMs make sure every part is right. Keeping temperature and humidity steady during checks also helps you get good results.
Tip: Real-time feedback and automatic checks save time and cut waste in making parts.
Material Selection
Picking the right metal is very important for net shape and near net shape. You want alloys that flow well and do not crack or stick to the die. Good flow helps the metal fill every part of the mold. Alloys that do not crack keep your parts strong as they cool.
You should also look at how strong the metal is. Alloys with high strength and stretch make strong, stable parts. Even grain size and low porosity help you keep tight fits. If you stop defects like gas bubbles or oxides, you get better net shape parts.
Manganese in alloys can help stop the die from sticking.
Better nucleation and grain changes make parts higher quality.
Changing things like shot speed can lower defects.
By picking the right metal and controlling the process, you can get very good net shape parts in your factory.
Benefits and Challenges
Reduced Waste and Cost
Net shape die casting helps you save a lot of material. The parts come out almost the right shape, so you only need to remove about 0.8mm. Old ways cut parts from big blocks and waste up to 90% of the metal. Net shape die casting uses just what you need. This is very helpful when metals are expensive. You also spend about 70% less time on rough cutting. If you use CNC finishing only on important areas, you get very exact parts (as close as ±0.05mm) and keep costs down. Die casting can make tricky shapes in one step. Other ways would waste more or be too hard.
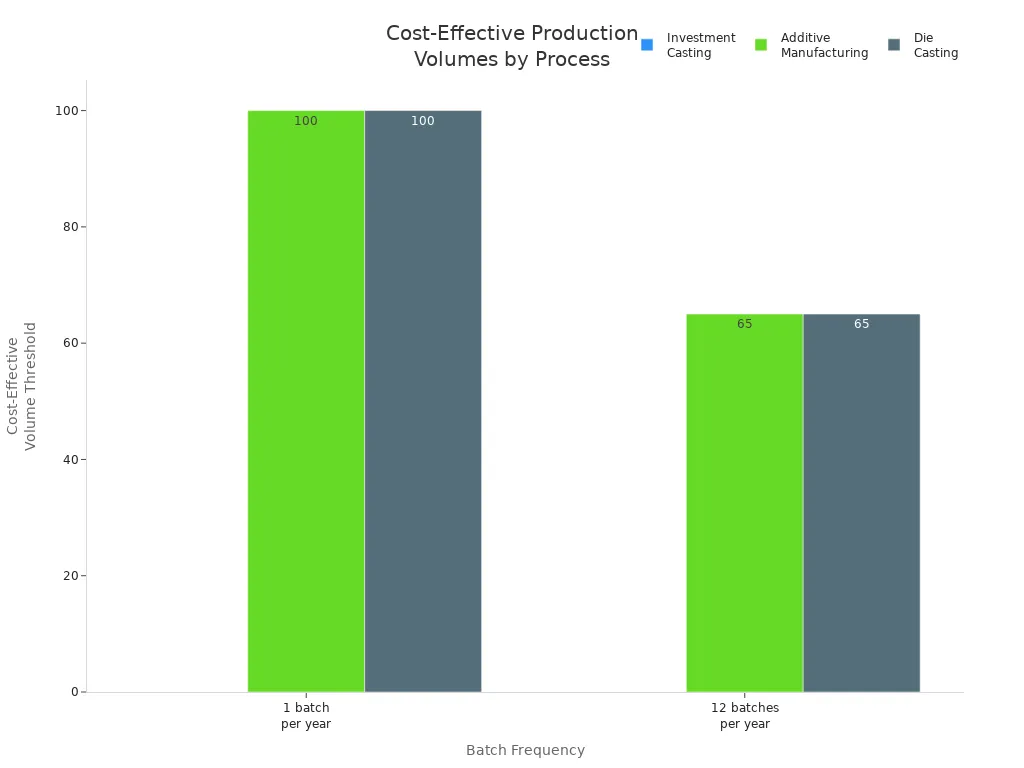
Process | Batches Per Year | Most Cost Effective Production Volume Range |
|---|---|---|
Investment Casting | 1 | Never cost-effective |
Investment Casting | 12 | Never cost-effective |
Additive Manufacturing | 1 | Cost-effective below ~100 parts |
Additive Manufacturing | 12 | Cost-effective below ~65 parts |
Die Casting | 1 | Cost-effective above ~100 parts |
Die Casting | 12 | Cost-effective above ~65 parts |
Die casting is best for making lots of parts. You can spread out the tool cost and make each part cheaper.
Efficiency and Lead Time
Net shape die casting lets you work fast and make many parts. You push hot metal into strong molds using high pressure. Each part takes only 1 to 30 seconds to make. You can make 10,000 or even 10 million parts. This is good for big jobs. The process uses machines, so you need fewer workers and get the same results every time. Molds last a long time, sometimes up to 1,000,000 uses. You do not need to stop often to change tools. Some companies can help with design, testing, and making parts all in one place. This makes your work go faster and smoother.
Net shape die casting helps you get products ready faster and saves money when you need lots of parts.
Common Limitations
Net shape die casting can have some problems. The molds are tricky and have many moving pieces and cooling parts. You must watch many settings, like how hot and fast the metal goes in. If you do not control these, you can get problems like bubbles or missing spots. Some shapes are hard to fill, like thin walls or sharp corners. Even with good design, some parts still need extra cutting to be perfect. Simulation tools can help you plan, but you need good data and skilled people to use them. Working with smart die casters and using new machines can help fix these problems, but you need to plan and work together.
Tip: Work early with skilled die casters and make smart design choices to get the best results from net shape die casting.
You get net shape in die casting by planning well and using smart design. Precise molds help make parts that are ready to use. Strong process control keeps everything working right. This way, you do not waste much material or need extra steps.
You can make parts with exact shapes and fine details.
You save money because you do not throw away much metal.
The process is fast, so you can make lots of parts quickly.
The parts look smooth and have a nice finish.
This method works for cars, planes, and electronics.
Use good planning and the best tools to reach your net shape goals.
FAQ
What is the main benefit of net shape die casting?
You get parts that are ready to use right out of the mold. This saves you time and money. You also waste less material, which helps the environment.
Can you use net shape die casting for complex parts?
Yes, you can make complex shapes with net shape die casting. Advanced molds and digital design tools help you create detailed parts with fine features.
How do you know if your part is a good fit for net shape die casting?
If your part needs tight tolerances, smooth surfaces, and high volume, net shape die casting works well. You should ask your die caster to review your design for best results.
Do net shape die cast parts always need no finishing?
Most net shape parts need little or no finishing. Sometimes, you may need to trim small bits or clean the surface. You rarely need extra machining or drilling.
See Also
Complete Walkthrough For Designing Die Casting CAD Models
Exploring Advantages Of CAE Simulation In Die Casting Design
An Overview Of Aluminum Extrusion And Die Casting Methods
Selecting Optimal Closing Force For Your Die Casting Product
Effects Of Thermal Stress On Die Casting Dies And Parts
About Hunan Puka
Established in 2016 and based in Hunan, China, with a liaison point in Berlin, we are a Tier 2 supplier for the automobile industry. We specialize in the production of customized aluminum die-casting parts designed for machines with a closing force ranging from 280 to 1250 tons, with subsequent manufacturing process CNC machining and surface treatment. Our commitment to quality is reflected in our accredited quality management system, certified by ISO9001:2015 and IATF16949:2016 standards.


