How the die casting industry supports the emerging robotics market with robotics parts and robotics material

Die casting is very important in the robotics industry. It helps make strong and exact robotics parts. Big companies like FANUC and ABB Robotics use advanced die casting. They do this to keep up with more orders. The global die casting market was worth $69.72 billion in 2024. It may grow to $112.27 billion by 2033. This growth happens because of new technology and more automation. There is also a high need for electric vehicles. Robotics parts made with die casting help with complex designs. They also help modern machines work better.
Benefits for Robotics
Precision and Consistency
Robotics needs parts that fit just right every time. Die casting helps make this happen. Makers control things like pouring temperature, mold temperature, and injection speed. This helps every part turn out the same. For example, when making an ADC12 aluminum alloy right crankcase cover, experts set the pouring temperature to about 680 °C. They set the mold temperature to about 200 °C. The injection speed is about 5 m/s. These settings help stop air bubbles and cracks. So, the process makes high-quality robotics parts with no visible problems. This control helps robots work better and last longer.
Durability and Strength
Robots often work in hard places. They need parts that can handle stress, heat, and long hours. Die casting gives these parts the strength they need. The process uses strong metals like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. These metals help make parts that do not break easily. Robots can lift heavy things, move fast, and keep working for a long time because their parts stay strong. This makes die casting a good way to build robots people can trust.
Efficiency and Cost Savings
Die casting also helps companies save money and work faster. Many factories use robots and smart machines to help with die casting. This makes the process quicker and safer. Here are some ways die casting saves energy and money:
Making machines run better can cut energy use by 10–20%.
In 2020, a 10% energy cut could have saved $288 million worldwide.
Smart planning during production can lower energy costs by almost 20%.
Most energy in die casting is used for melting and moving metal, so making these steps better saves the most.
Automation in die casting can help make more parts and stop up to 90% of defects. Robots also make the workplace safer by reducing accidents by up to 98%. These changes mean companies can make more robotics parts for less money and with better quality.
Cost Factors Influencing Die Casting | Optimization Strategies for Cost Savings and Efficiency |
|---|---|
Mold costs | Design optimization |
Material costs | Material selection |
Machine costs | Tooling and mold design |
Labor fees | Production volume optimization |
Other overheads | Automation, process monitoring, energy efficiency |
Waste reduction, continuous improvement |
Robotics Parts Made by Die Casting

Structural Components
Die casting is important for making strong robot parts. These parts help hold robots together. Factories use high-pressure die casting to shape metals. They use aluminum and magnesium for frames, arms, and joints. These metals make parts strong and light. This helps robots move fast and lift heavy things.
The quality of these parts depends on many things. Higher injection pressure makes aluminum parts harder and denser. Special coatings on the die make it last longer. Oil cooling makes parts harder than air or water cooling. Factories use sensors to check pressure inside the mold. This helps stop mistakes and keeps parts stable.
Gas bubbles can make parts weak. Better venting and vacuum systems help remove gas. This makes parts last longer in robots.
Here is a table that shows how different steps change robot parts:
Process Parameter | Effect on Material Property | Quantitative Evidence / Observation |
|---|---|---|
Injection Pressure | Increases density and hardness; reduces porosity | Higher injection pressure reduces porosity and increases density and hardness in LM24 aluminum alloy castings. |
Die Coating | Improves hardness and die life | Use of dycote coating increases hardness; coatings prevent molten metal sticking and improve die life. |
Cooling Method | Influences hardness | Oil cooling enhances hardness more than air or water cooling. |
Alloy Composition | Affects ductility and yield strength | Al-Si and Al-Mg alloys achieve high ductility (>12% elongation) and yield strength (>120 MPa) with heat treatment. |
Microstructure | Crack propagation linked to injection pressure | Low injection pressure samples show crack propagation; microstructure affected by pressure during solidification. |
Venting and Vacuum | Controls gas porosity and improves tightness | Proper venting and vacuum systems reduce gas porosity, enhancing product quality and reliability. |
In-cavity Pressure Sensors | Optimize casting parameters | Sensors help monitor and adjust process to reduce defects and improve dimensional stability. |
Coating Types | Enhance die surface resistance and cycle life | Hard coatings (carbides, nitrides) protect die steel from erosion and soldering; ZrO2 and WC-Co coatings reach 45000 cycles without damage. |
High-pressure die casting alloys like Al-Si and Al-Mg are very strong. With heat treatment, Al-Si alloys can be even stronger. They can stretch more than 12% and have proof strengths over 400 MPa. These features help robots do hard jobs and stay safe if they crash.
Internal Mechanisms
Die casting also helps make small robot parts inside. These parts include gears, brackets, and levers. They help robots move and work. Factories use die casting to make tiny, detailed shapes. This makes sure each part fits and works well.
Robots need inside parts that last a long time. Die casting uses strong alloys for these parts. The smooth surfaces from die casting lower friction. This helps robots move quietly and easily. Factories can make many of these parts fast. This keeps costs low and quality high.
Many robot parts need these inside pieces to work fast and right. Good inside parts help robots work longer without breaking.
Housings and Enclosures
Housings and enclosures keep robot parts safe. Die casting helps make these parts with great detail. Factories can make shapes that fit tightly around robot parts. This keeps out dust, water, and other things that can hurt robots.
Here is a table that shows what makes good housings and enclosures for robots:
Metric / Factor | Description / Relevance to Robotics Die Casting Housings and Enclosures |
|---|---|
Precision and Repeatability | Ensures consistent manufacturing of parts with tight dimensional tolerances for reliable robotic use. |
Dimensional Tolerances | Tight tolerances enable exact specifications for complex designs, critical for robotics components. |
Surface Finish Quality | High-quality finishes improve durability and performance of housings and enclosures. |
Mechanical Property Testing | Tests such as strength and wear resistance confirm robustness under operational stresses. |
Durability and Wear Resistance | Components withstand harsh conditions and prolonged use in robotics applications. |
Compliance with Industry Standards | Adherence to ISO and other standards guarantees product reliability and acceptance. |
Advanced Design Simulation | Mold flow and stress analysis reduce defects and optimize part performance and longevity. |
Automation and Robotics Integration | Enhances production efficiency and consistency in manufacturing processes. |
Lean Manufacturing Principles | Reduces waste and production costs while maintaining quality and delivery speed. |
Inspection Methods | X-ray testing and dimensional analysis ensure defect-free, precise components. |
Use of Lightweight, Robust Materials | Aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys provide strength without excess weight, ideal for robotics. |
Customization Capability | Ability to produce complex, tailored parts for specific robotic applications and harsh environments. |
Die casting uses light but strong materials like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium. These keep robots quick and protect their important parts. Factories use design simulations and careful checks like X-ray testing. This makes sure each housing meets the rules. These steps help robot parts last in tough places and work for a long time.
Custom die-cast housings and enclosures protect robots and allow special designs. This helps robots meet new needs in the growing market.
Materials for Robotics
The robotics industry needs advanced materials for strong, light, and exact parts. Die casting uses metals that help robots move fast and last long. These metals also help robots work better. The main materials are aluminum alloys, zinc alloys, and magnesium alloys.
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys are used a lot in robotics. They are light and strong. High-pressure die casting shapes these alloys into exact parts. These parts have smooth surfaces and tight fits. Robots need these features to move fast and right. High-pressure die casting makes parts quickly and with little waste. This helps keep costs down.
Robotics parts made from aluminum alloys are strong and last long. They do not wear out or break easily. These alloys can be used for small gears or big frames. The table below lists some aluminum alloys used in robotics:
Alloy | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
A380 | ~160 | ~324 | ~3.5 | Balanced strength and ductility, excellent castability and corrosion resistance |
A383 | ~151 | ~310 | ~3.5 | Higher silicon content improves fluidity and reduces shrinkage porosity |
B390 | ~250 | ~400 | ~1.0 | High wear resistance and dimensional stability, suitable for high hardness parts |
A360 | ~170 | ~317 | ~5.0 | Good castability and corrosion resistance, higher strength but lower ductility than A413 |
A413 | ~130 | ~290 | ~8.0 | Excellent ductility and impact resistance, good for intricate castings |
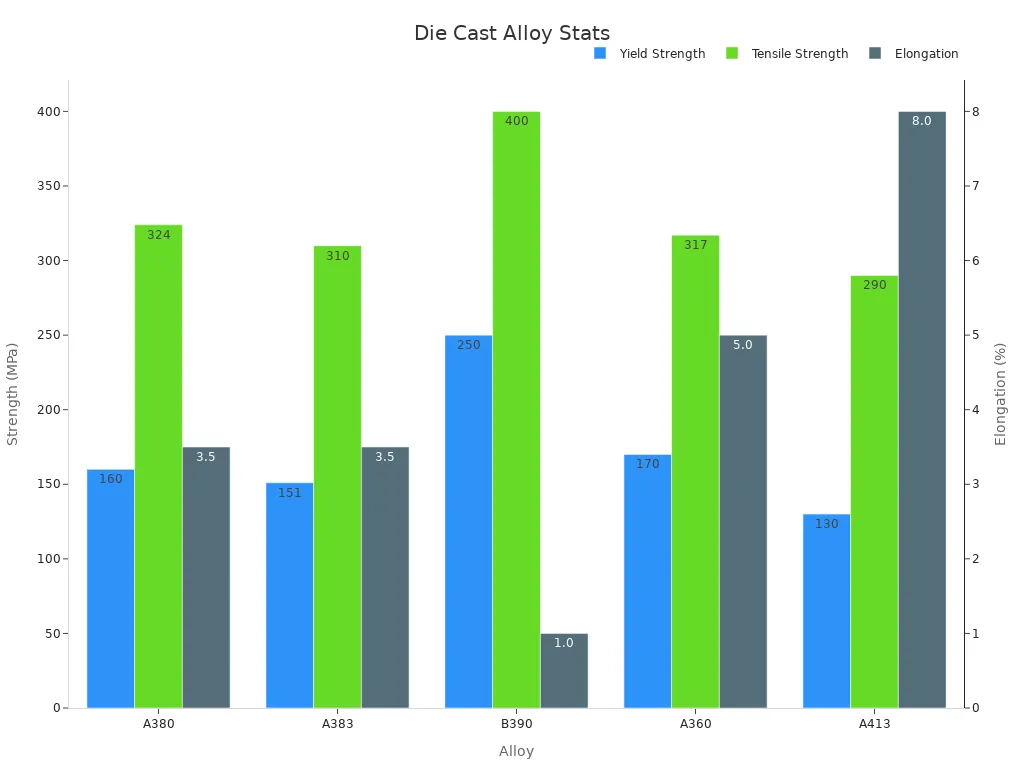
High-pressure die casting aluminum parts help robots move in complex ways. These parts are light and reliable.
Zinc Alloys
Zinc alloys are great for making small, detailed robot parts. They are easy to shape into gears, connectors, and housings. Zinc parts do not rust or wear out fast. This means they last a long time. Factories can make many zinc parts quickly. This helps meet the need for more robots.
Zinc alloys are cheap for making lots of parts.
They let electricity flow well, which helps some robot parts.
Zinc melts at a low temperature, so it saves energy.
Magnesium Alloys
Magnesium alloys are the lightest metals used in robotics. They help make robot arms and frames lighter. This makes robots move faster and use less energy. New studies show rare-earth magnesium alloys, like WE43, are strong and bend well. These things are important for parts that must be tough and flexible.
Scientists use new tools, like machine learning, to design magnesium alloys. They try to get the right mix of strength and bending. This helps robots do hard jobs. Magnesium alloys also make smooth and exact parts. These are needed for moving robot parts.
Magnesium die casting helps make robots lighter and quicker. This is good for factories and service robots.
Key Market Insights:
Asia Pacific is the top area for metal casting robots.
Growth comes from more car factories and more people with money in India and China.
Metric | Value (USD Million) | Period |
|---|---|---|
Market Size | 2,217.4 | 2023 |
Market Size | 2,317.2 | 2024 |
Market Size | 3,633.8 | 2032 (forecast) |
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) | 5.8% | 2024-2032 |
These materials help robotics companies make safer and better robots every year.
Automation in Die Casting

Automation has changed how factories make die cast parts. Robots now help with many steps. This makes making parts faster and safer. It also makes the process more reliable.
Robotic Handling
Robotic handling systems move hot metal parts safely. These robots pick up castings and put them on conveyors. They also move parts into cooling tanks. Robots help with machine tending and checking parts. This lowers mistakes and keeps workers safe from burns.
AI-powered robots, like the RTH-2TP and RWH-3DF, finish surfaces very well.
Robotic cutting and sandblasting systems lower mistakes and make parts the same.
Automated machine tending helps with steady handling and careful checking.
Robotic handling helps make the same part every time. It also lowers defects and helps with quality control.
Material Feeding
Automated material feeding systems bring metal to the machines. Robots control how much metal goes into the molds. This keeps each part the same and cuts down on waste.
Automated feeding makes production faster and stops delays. Robots feed metal quickly and with care. This helps make more parts in less time. Workers can check machines and fix problems instead of repeating tasks. This also keeps people away from hot or risky places.
Automated feeding systems help factories make more parts. They also save money and keep workers safe.
Trimming and Finishing
After casting, parts need trimming and finishing. Robots now do these jobs with great care. Robotic presses and arms use special tools to cut and smooth parts. This makes sure every part is the right size and shape.
Robotic deburring and trimming systems make parts smooth. They also keep workers safe from sharp tools and flying bits. Sensors and AI check each part for problems and measure its size. Only the best parts move forward, so there is less waste.
Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
Precision | Robots trim parts to exact sizes |
Safety | Fewer injuries from sharp tools |
Quality Control | Sensors and AI check for defects |
Speed | Faster finishing than manual work |
Automated trimming and finishing help factories make better robotics parts. These parts last longer and work better.
Die casting helps make robotics parts that are strong and exact. This lets robots do their jobs better and last longer. Many companies use new machines and mold designs to make more parts.
The aluminum die casting market could grow from $49.66 billion in 2025 to $67.94 billion by 2030.
More factories use robotics to make parts quicker and with fewer errors.
More cars and machines being made means we need better robotics parts.
These changes show that both industries can help each other. Companies should look into die casting to meet their robotics needs.
FAQ
What is die casting?
Die casting is when factories push melted metal into a mold. This makes parts that are strong and fit well. Many companies use die casting to make parts fast. It also helps them waste less material.
Why do robotics companies choose die casting for parts?
Robotics companies like die casting because it makes strong and light parts. These parts help robots move better and last longer. Factories can also make lots of parts quickly.
Which metals work best for die casting in robotics?
Metal | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
Aluminum | Lightweight, strong |
Zinc | Good for small parts |
Magnesium | Very light |
These metals help robots do many different jobs well.
How does automation improve die casting?
Automation uses robots to move hot metal and feed machines. Robots also help finish the parts. This makes the work safer and faster. Robots help stop mistakes and keep the parts good.
See Also
Essential Trends Shaping The 2025 Automotive Aluminum Casting Industry
Understanding The Functioning Of Aluminum Extrusion And Casting Methods
Comprehensive Walkthrough For Designing Die Casting In CAD Software
Methods To Identify Optimal Closing Force For Die Casting Products
Exploring Advantages Of CAE Simulation In Die Casting Engineering
About Hunan Puka
Established in 2016 and based in Hunan, China, with a liaison point in Berlin, we are a Tier 2 supplier for the automobile industry. We specialize in the production of customized aluminum die-casting parts designed for machines with a closing force ranging from 280 to 1250 tons, with subsequent manufacturing process CNC machining and surface treatment. Our commitment to quality is reflected in our accredited quality management system, certified by ISO9001:2015 and IATF16949:2016 standards.


