What is an Automated Die Casting Island and How Does it Work

A die casting island is a system that works by itself. It uses many machines, robotic arms, and computers to do high pressure die casting. This setup lets workers collect data and watch each step as it happens. An automated die casting island uses special tools like CT scanning and computer-aided engineering. These tools help find problems, change settings, and make sure the parts are good.
Robots and sensors work together to move parts, check quality, and control heat.
The island uses number data to work better and lower mistakes in casting.
This way helps factories follow strict rules in modern manufacturing.
Die Casting Island Components

Die Casting Machines
Die casting machines are the main part of the system. They push hot metal into molds using high pressure. Modern machines use PLCs to control each step. PLCs help make quick and exact changes. In advanced islands, machines share data right away through digital links. This helps make more good parts. For example, low-pressure die casting can make 90-95% good parts. This is better than old ways. Big machines like giga presses make large aluminum parts fast and well.
Robotic Systems
Robotic systems do many jobs in these islands. Robots move parts, pour metal, and take out finished pieces. They work very carefully, even with tricky or shiny parts. Some robots use 3D vision to see and grab things without harm. Robots also check quality and sort parts. These robots help make work more exact and faster. They do the same job the same way every time. In tough places, robots use special covers and controls to stay safe.
Automation Control
Automation control links all the parts together. Central control uses PLCs, HMIs, and SCADA software. These tools watch and change machines and robots as they work. Automation control can save up to 30% energy by turning off things not in use. Flexible programs let some parts rest when not needed, cutting waste. Remote checks and fixes make the process smoother and more steady.
Sensors and Software
Sensors and software are very important in smart factories. Sensors watch heat, pressure, and speed at every step. They send this data to software for study. For example, a smart factory in Korea used sensors and software to watch casting and find problems early. Advanced tools like machine learning help engineers pick the best settings. In Japan, sensors and software kept furnace heat steady, saving energy and making parts more even. These tools help watch in real time and fix problems fast, making robotized systems better and quicker.
Note: When machines, robots, controls, sensors, and software work together, they make a live network. This network is the main part of modern die casting automation and smart factories.
Automated Die Casting Cells Process

Metal Handling
The automated die casting cell starts with metal handling. Workers or machines get the raw materials ready. They crush, shred, and sort recycled aluminum. Robots put the metal into melting furnaces. The furnaces heat the metal from 425°F to 600°F. Sensors check the temperature to keep it steady. Automated systems add salts and dry gases like nitrogen or argon. These remove oxides and hydrogen. This step stops holes from forming in the final part. Robots and conveyors move the hot metal to the next step.
Tip: Engineers use 3D CAD design and simulation tools to plan the cell layout. This planning helps robots reach and handle parts better. It cuts down on waiting and boosts how many parts are made.
Process Stage | Quantitative Data / Parameters | Notes / Description |
|---|---|---|
Metal Handling | Raw material crushed, shredded, sorted | Initial preparation of recycled aluminum materials |
Melting | Furnace temperature: 425°F to 600°F | Use of induction, crucible, or electric furnaces |
Oxide Removal & Degassing | Addition of salts and dry gases (N2, Ar, Cl2) | Removes oxides and hydrogen to prevent voids |
How fast the metal cools affects cycle time in automation. Robots and software work together to make this timing better. This helps make more parts and less waste.
Robots use data from CAD models to pick the right tools.
Robotic simulation helps set up the cell and save time.
Better casting yield means less waste and lower energy use.
Injection and Casting
After melting, the hot metal goes to injection and casting. A die casting machine pushes the metal into a mold at high pressure. The process uses exact numbers: pouring temperature is 730°C, die temperature is 400°C, and flow rate is 9.1·10⁻⁵ m³/s for 2.6 seconds, then slower for 0.4 seconds. Sensors and software watch these numbers as the process runs.
Automation makes sure the metal fills the mold fast and even. Robots may spray lubricant on the die. This keeps the metal from sticking and makes the surface smooth. The system checks metal flow with over 870,000 cubic cells. This helps find problems like oxide spots. This control keeps quality high in high pressure die casting.
Process Stage | Quantitative Data / Parameters | Notes / Description |
|---|---|---|
Metal Injection | Pouring temp: 730°C; Die temp: 400°C; Flow rate: 9.1·10⁻⁵ m³/s | Cold chamber process typical for aluminum; precise control for quality |
Die Lubrication | Automatic spray lubrication | Prevents casting adherence to die, improves finish |
Extraction and Machining
When the metal cools, robots take the casting out of the die. Sensors check if the part is cool enough to move. Automated arms carry the part to the next station for machining. Machining cuts off extra material and shapes the part.
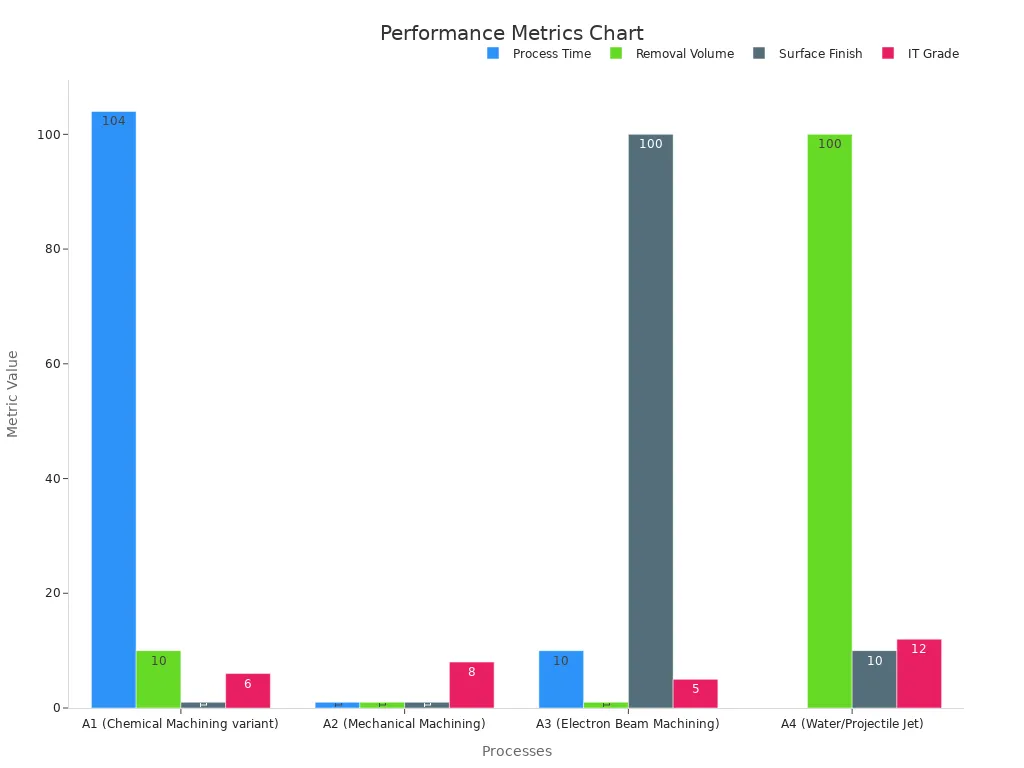
Different machining types have different speeds and finishes. Mechanical machining can remove 1 mm³ of material in 1 second. It gives a smooth finish and tight fit (IT grade 8). Chemical machining is slower but even more exact. Robots do these jobs fast and safely. This lowers the chance of damage.
Process | Process Time (s) | Material Removal Volume (mm³) | Surface Finish (μm) | IT Grade (Tolerance) | Energy Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Chemical Machining | 104 | 10 | 1 | 6 | Chemical | High precision, smooth finish |
Mechanical Machining | 1 | 1 | 1 | 8 | Mechanical | Fast, tight tolerances |
Electron Beam Machining | 10 | 1 | 100 | 5 | Radiation | Moderate speed, rough finish |
Water/Projectile Jet | N/A | 100 | 10 | 12 | Mechanical | High removal rate, rough finish |
Quality Control
Quality control is the last step in the automated die casting cell. Sensors collect data on pressure, temperature, and cooling at each step. The system uses time series data to spot changes or odd patterns. Robots and cameras check the parts by looking at them. Sometimes, they use X-ray images to find hidden defects like porosity. Machine learning studies the data and inspection results. It predicts problems and suggests fixes.
Each part gets a digital mark that links it to its data. This lets engineers trace any problem back to where it started. Combining machine data, die sensors, and alloy checks helps smart factories make good, reliable parts.
Process Feature Group | Description | Role in Quality Control and Reliability |
|---|---|---|
Pressure, temperature, cooling data segmented into phases | Supports process monitoring and yield improvement | |
Visual Inspection (X-ray) | Inspection of cast parts for porosity defects | Detects internal flaws |
Machine Learning Models | Classification algorithms on process data | Predicts defects and tunes process |
Part Tracking and Data Integration | Digital timestamping and marking | Links process data to inspection results |
Note: Using robots, real-time sensors, and smart software makes die casting automation important for modern factories. This way improves quality, saves time, and helps track each part from start to finish.
Die Casting Automation Benefits
Efficiency
Die casting automation helps factories work faster and better. Machines and robots do jobs all day and night. This keeps the production line moving without stopping. In 2023, the market for automated metal casting machines was worth $4.5 billion. Experts think it will reach $9.0 billion by 2032. This means companies really care about working efficiently.
Metric | Value | Insight |
|---|---|---|
Market Size (2023) | USD 4.5B | Starting value for automated metal casting machines |
Projected Market Size (2032) | USD 9.0B | Market could double in 9 years |
Compound Annual Growth Rate | 8.0% | Automation demand is making the market grow fast |
Growth Drivers | Productivity, labor cost reduction, precision, consistency | Companies want to save money and make better products |
Many factories in rich countries have over 70% of their die casting automated. This helps them when there are not enough workers. Robots and software keep the work going quickly and smoothly. This means companies can make more parts in less time.
Quality
Die casting automation makes products better in many ways. Automated systems use sensors and cameras to check each part. They find problems right away and help fix them fast. Companies can make 33% more parts when they use automation. Robots do almost all the hard jobs, so there are fewer mistakes.
Simulation software helps stop problems like cold laps and hot spots.
Automated systems keep the timing the same, so every part is made right.
AI quality control finds problems quickly and helps keep waste low.
These steps help factories meet tough rules and send out good products.
Safety
Automation makes die casting safer for workers. Robots move hot metal and heavy things, so people stay away from danger. Sensors watch for unsafe things and can stop machines if needed. This lowers the chance of burns, cuts, or other injuries. Workers can do safer jobs, like watching screens or checking data.
Tip: Automated safety checks and emergency stops help keep everyone safe.
Cost Savings
Factories save a lot of money with die casting automation. Automation can make lead times shorter by up to 89% and cut costs by 60%. Robots and smart systems use less energy and make less waste. Companies spend less fixing machines because they can spot problems early. These savings help businesses stay strong and buy better machines for the future.
Die Casting Operations Challenges
Investment
Automated die casting islands need a lot of money at first. Companies have to buy advanced machines, robots, and control systems. These tools cost much more than simple equipment. Many factories also must upgrade their power and cooling systems. Training workers to use new technology adds more cost. Some companies cannot get enough money for these changes. The high price can make automation slow, especially for small businesses.
Note: Companies often plan for years before spending so much. They think about saving money and making better products to explain the cost.
Maintenance
Keeping automated die casting equipment working well is hard. Machines like gears, bushings, and circuits wear out over time. If companies skip regular maintenance, machines can break down. This causes unplanned stops, lower quality, and higher costs. For example, a Dodge Durango plant had no downtime for three years with good maintenance. But a Hyundai plant had about 20% downtime from poor maintenance. One hour of downtime can cost over $100,000 in lost production. These facts show why regular maintenance is very important for automated systems.
Flexibility
Automated die casting islands can have trouble with new part designs or changes. Old setups can be stiff, so it is hard to switch products. New solutions help make systems more flexible. Modular machine designs let companies change tie bar distances and injection forces. They do not need to buy new machines. Melting and dosing parts can be mixed for different needs. Smart shot control and digital process tools help cut waste and make parts more even. The table below shows ways companies make systems more flexible:
Flexibility Measure | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
Modular Machine Design | Change machine modules for new parts | Adapts to new designs |
Modular Melting/Dosing Components | Mix and match melting and dosing units | Customizes for different products |
Intelligent Shot Control | Adjusts metal flow automatically | Reduces defects and scrap |
Uses data to find and fix problems | Increases productivity and reduces waste |
Tip: Remote support and AI control systems help companies fix problems fast and keep production running.
A die casting island uses machines, robots, and smart controls. These work together to make metal parts fast and safe. This system helps factories finish jobs quicker. It also helps them make better products. Workers stay safer because robots do the hard jobs. Many companies save money and get higher quality with this system.
Any factory can use a die casting island to get better at die casting.
Companies that use automation are often leaders in new manufacturing.
FAQ
What is the main job of a die casting island?
A die casting island makes metal parts by using machines, robots, and computers. It controls each step, from melting metal to checking finished parts. This setup helps factories work faster and make better products.
How do robots help in die casting automation?
Robots move hot metal, take out finished parts, and check quality. They work with sensors and software to keep each step safe and exact. Robots also help lower mistakes and keep workers away from danger.
Can a die casting island make different parts?
Yes, a die casting island can make many types of parts. Factories use modular machines and smart controls to change settings. This lets them switch between products without buying new equipment.
Why do factories use sensors in die casting?
Sensors watch heat, pressure, and speed during casting. They send data to computers for quick checks. This helps find problems early and keeps each part within quality limits.
Is it hard to keep an automated die casting island running?
Keeping the system running needs regular checks and care. Workers must watch machines, fix small issues, and follow a maintenance plan. Good care helps avoid breakdowns and keeps production steady.
See Also
Understanding The Basics Of Aluminum Extrusion And Die Casting
Complete Stepwise Instructions For Designing Die Casting CAD Models
Exploring Anodizing Techniques Used In Die Casting Products
Reasons The 1250T Die Casting Machine Suits Large Scale Projects
Understanding Functional Testing Procedures In CNC And Die Casting
About Hunan Puka
Established in 2016 and based in Hunan, China, with a liaison point in Berlin, we are a Tier 2 supplier for the automobile industry. We specialize in the production of customized aluminum die-casting parts designed for machines with a closing force ranging from 280 to 1250 tons, with subsequent manufacturing process CNC machining and surface treatment. Our commitment to quality is reflected in our accredited quality management system, certified by ISO9001:2015 and IATF16949:2016 standards.


